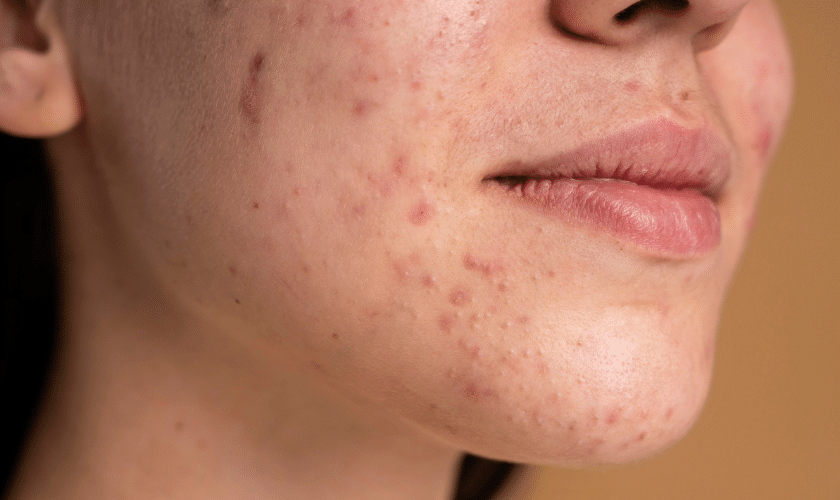
Acne affects millions worldwide, transcending age and gender. Whether you’re a teenager battling hormonal changes or an adult dealing with persistent breakouts, understanding acne is the first step towards clearer, healthier skin. In this guide, we delve deep into the causes, treatments, and prevention strategies to help you combat acne effectively.
The Basics of Acne
Acne, medically termed acne vulgaris, is a common skin condition characterized by the presence of pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, and cysts. These blemishes typically appear on the face, neck, chest, shoulders, and back. The condition arises when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, leading to the formation of lesions.
Understanding Acne Causes
Several reasons contribute to the development of acne:
Hormonal Fluctuations: Fluctuations in hormone levels, especially during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, can trigger acne.
Stress: Stress can exacerbate acne by triggering hormonal changes and increasing inflammation in the body.
Excess Oil Production: Overactive sebaceous glands produce an abundance of oil, which can clog pores and promote acne formation.
Genetics: While genetics alone don’t determine whether you’ll develop acne, they can predispose you to the condition. If your parents struggled with acne, there’s a higher likelihood that you will too.
Diet: Consuming high-glycemic foods, dairy products, and foods rich in saturated fats may contribute to acne development in some individuals.
Skincare Products: Using comedogenic or pore-clogging skincare products can worsen acne by blocking pores and trapping bacteria.
Environmental Factors: Exposure to pollutants, humidity, and certain medications can also aggravate acne symptoms.
The Types of Acne
Not all acne is created equal. There are various types, each with its own characteristics and severity levels.
Mild Acne: Characterized by blackheads, whiteheads, and small pimples, mild acne typically responds well to over-the-counter treatments and lifestyle changes.
Moderate Acne: Involves more inflamed lesions, such as papules and pustules. It may require prescription medications or dermatological interventions for effective management.
Severe Acne: This includes nodules and cysts, deep, painful lesions that can cause scarring if not treated promptly and properly.
Effective Treatments for Acne
Fortunately, several treatment options are available to manage acne and improve skin clarity. These include:
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments such as benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, and retinoids are commonly used to unclog pores, reduce inflammation, and prevent new acne lesions. These medications work by targeting the factors that contribute to acne development, helping to clear existing breakouts and prevent future ones.
Oral Medications
In severe cases of acne, oral medications like antibiotics, oral contraceptives, and isotretinoin may be prescribed. Antibiotics help to reduce bacterial growth and inflammation, while oral contraceptives can regulate hormone levels and minimize acne flare-ups in women. Isotretinoin, a potent medication derived from vitamin A, is reserved for severe, treatment-resistant acne and works by reducing oil production, shrinking oil glands, and preventing acne formation.
Procedures
In addition to topical and oral medications, various procedures can help manage acne and improve skin texture. These include:
Chemical Peels: Chemical peels exfoliate the skin, remove dead cells, and unclog pores, reducing acne lesions and improving overall skin tone and texture.
Laser Therapy: Laser therapy targets acne-causing bacteria, reduces oil production, and promotes collagen production, leading to clearer, healthier skin.
Extraction: Manual extraction of comedones (blackheads and whiteheads) by a medical dermatologist can effectively clear pores and prevent further breakouts.
Prevention Tips for Acne
While treating acne is essential, prevention is equally crucial for maintaining clear, healthy skin. Here are some tips to help prevent acne flare-ups:
Maintain a Consistent Skincare Routine: Maintain a Consistent Skincare Routine: Wash your skin twice daily with a mild cleanser and use non-comedogenic moisturizers and sunscreen to keep the skin hydrated and protected.
Avoid Touching Your Face: Touching your face can transfer bacteria, dirt, and oils to your skin, increasing the risk of acne breakouts. Avoid picking or popping acne lesions, as this can lead to scarring and further inflammation.
Watch Your Diet: Limit your intake of high-glycemic foods, dairy products, and foods high in saturated fats, as these can exacerbate acne symptoms in some individuals.
Manage Stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to minimize stress-related hormonal fluctuations and prevent acne flare-ups.
Choose the Right Products: Opt for skincare products labeled non-comedogenic, oil-free, and fragrance-free to minimize pore-clogging and irritation.
Understanding acne empowers you to take control of your skin health and achieve clearer, smoother skin. By addressing the root causes, exploring effective treatments, and implementing preventive measures, you can say goodbye to stubborn breakouts and embrace a complexion you’ll love. Consulting with a dermatologist can provide personalized guidance and treatment plans tailored to your specific needs, ensuring optimal results and long-term skin health.